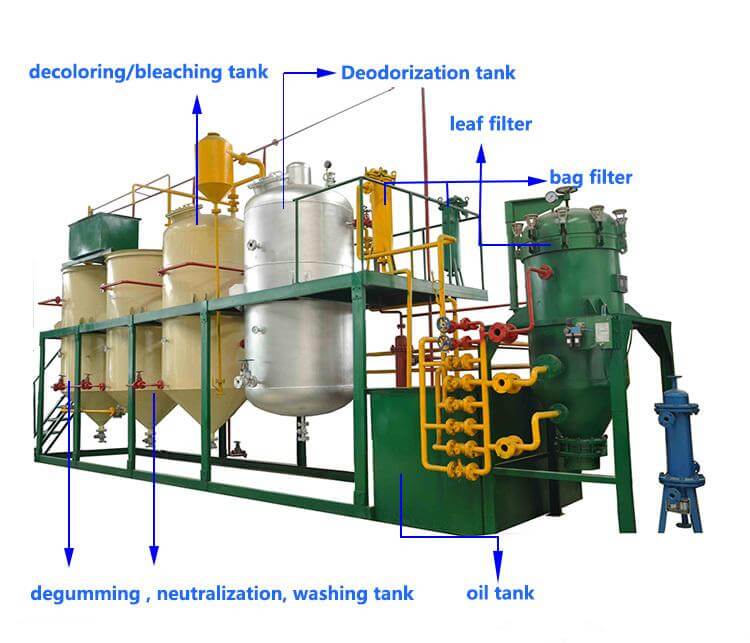
Complete solution for Batch & Continuous type Edible Oil Refinery Plant
Edible oil refining, A collective name for a series of processes that remove solid impurities, free fatty acids, phospholipids, colloids, waxes, pigments, odors, etc. contained in vegetable oil.
The refinery plants process the oil in a series of procedures like neutralizing, bleaching and deodorizing.
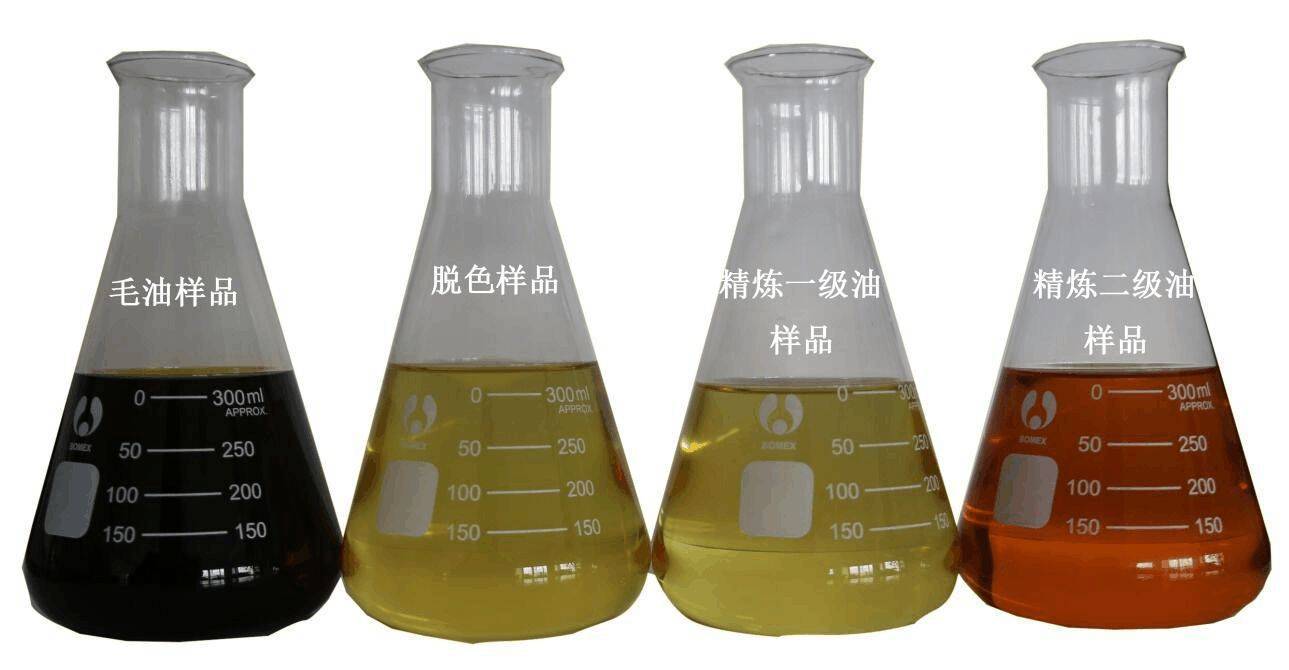
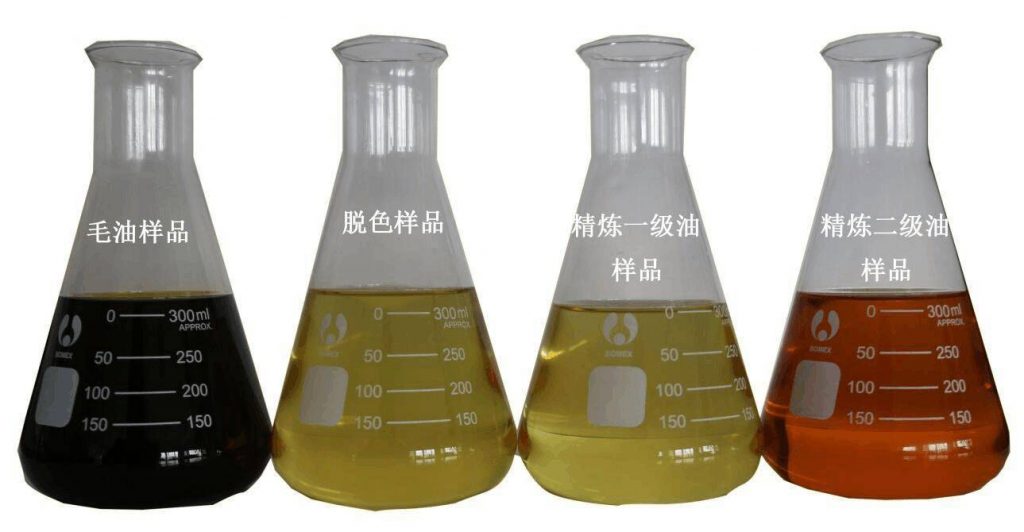
The oil finally produced from the processing plant is of god quality with light color. Also, we take care that free fatty acids present in oil can be also filtered out for edible grade. In addition to this, for sunflower and rice bran oil, an addition process of dewaxing is also carried out for separating our wax.
Edible Oil Refining Process
(1) Degumming: The process of removing peptidic impurities from crude oil using physical, chemical or physicochemical methods is called degumming. In edible oils and fats, if the phospholipid content is high, they will easily foam, smoke, and have a smell when heated. Moreover, the phospholipids will oxidize at high temperatures, causing the oil to turn brown, which will affect the flavor of fried foods. Degumming is based on the principle that phospholipids and some proteins are soluble in oil in the sewage state, but are insoluble in oil after forming hydrates with water. Add hot water or water vapor to the crude oil, heat the oil and stir at 50°C. Mix, then let stand and separate the water phase to remove phospholipids and part of the protein.
(2) Deacidification: Free fatty acids affect the stability and flavor of oil. Free fatty acids can be removed by neutralizing with alkali, which is called deacidification, also known as alkali refining.
(3) Decolorization: Crude oil contains pigments such as chlorophyll and carotenoids. Chlorophyll is a photosensitizer and affects the stability of oil. Other pigments affect the appearance of oil and can be removed with adsorbents.
(4) Deodorization: There are some unwanted odor substances in oil, which are mainly derived from oil oxidation products. Use vacuum distillation and add citric acid to chelate excessive metal ions and inhibit oxidation.
Edible Oil Refining Flow chart
Crude oil → Filtration → Degumming → Deacidification → Vacuum drying → Decolorization → Deodorization → Filtration → Refined edible oil
Soybean oil, peanut oil, and sesame oil are the bulk oils in my country. If the raw material quality is good and the oil extraction process is reasonable, the quality of the crude oil is better, the free fatty acid content is generally less than 2%, and it is easy to refine.
Soybean Oil Refining
Crude oil → Filtration → Degumming → Deacidification → Vacuum drying → Decolorization → Deodorization → Filtration → Refined edible oil
Cottonseed oil is also a major cooking oil. However, cotton wool oil contains gossypol (content of about 1%), gum and wax of poor quality and is not suitable for direct consumption, and its refining process is also relatively complex.
Cottonseed Oil Refining
Filter crude oil—→preheat—→oil-alkali ratio—→mixing reaction—→desoap—→wash—→dehydration—→dry—→cotton clear oil
Deodorized cotton oil—→cooling and crystallization—→crystallization—→filtration
Rapeseed Oil Refining
Filter rapeseed oil—→Preheat—→Neutralize—→Let stand and settle—→Separate—→Wash←—Soft water
↓
Filtration←—distillation deodorization←—filtration←—adsorption decolorization←—dehydration
Rice Bran Oil Refining
Filter the bran oil—→pretreatment—→primary neutralization—→separation—→secondary neutralization—→separation—→washing
↓
Refined rice bran oil ←—filtration ←—cooling and crystallization ←—distillation and deodorization ←—filtration ←—adsorption and decolorization ←—dehydration
Palm Oil Refining
Filter crude palm oil—→preheat—→neutralize—→leave to settle—→separate—→wash with water←—soft water
↓
Filtration←—distillation deodorization←—filtration←—adsorption decolorization/bleaching←—dehydration
Palm kernel oil and coconut oil are non-drying oils. The fatty acid composition is dominated by lauric acid (accounting for 45% to 5l% of the fatty acid composition), followed by myristic acid (accounting for about 13% to 25%). The colloid content is low, and it is especially suitable for physical refining and deacidification.
Copra Oil Refining
Crude oil—→dry degumming—→filtration—→deacidification/deodorization—→filtration—→refined oil
Sunflower Oil Refining
Filter crude oil—→Preheat—→Mix—→Oil-alkali ratio—→Mixing reaction—→Desoap—→Soap stock
↓
Wax paste←—filtration←—cooling crystallization←—distillation deodorization←—filtration←—adsorption decolorization←—drying←—dehydration←—washing←—soft water